COM Express: Finding the Right Type
COM Express is a family of modular, small-form-factor computer-on-module (COM) specifications defined by the PCI Industrial Computer Manufacturers Group (PICMG). A nonprofit consortium of companies and organizations, PICMG collaboratively develops open standards for high-performance telecommunications, military, industrial, and general-purpose embedded computing applications.
Benefits of COM Express
The goal of the COM Express specification is to fill the computing gap between high-cost, high-performance devices and low-cost, Raspberry Pi-like devices. This modular system allows mid-range processing and networking capabilities, that can be applied to automation, transportation, robotics, medical, and other technology-driven markets.
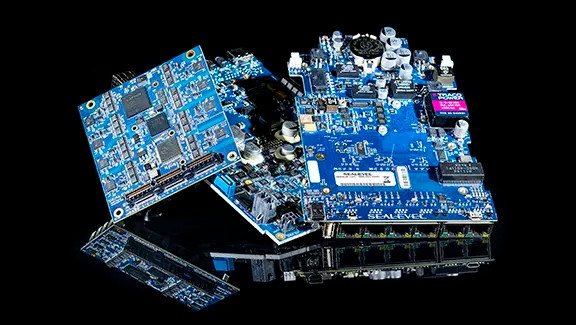
The major feature that separates COM Express boards from traditional single-board computers, is the flexibility to mix-and-match various off-the-shelf modules. Essentially, a complete carrier board or baseboard is custom designed to meet the application’s I/O or subsystem requirements, and a COM Express processor module attaches directly to the board.
Further, as new COM modules are released, they can easily be integrated into the existing carrier board, allowing for a large degree of backward compatibility. By utilizing a two-board system – the carrier board with all the I/O and various subsystems, and the COM Express processor module containing the CPU and other processing components – engineers can develop, design, and test more rapidly for faster time to market. Designs are easily upgraded as new processors are released.
COM Express Types
The initial COM Express design was published in 2005 and has since become one of the more popular embedded hardware standards in the world. To date, PICMG has released eight different COM Express Types, four different sizes, and three major revisions.
Among the eight different COM Express specifications, Types 6, 7, and 10 are the most widely used. These three designs account for the majority of current COM Express applications, and they come in four main sizes: Mini, Compact, Basic, and Extended. There are a few major differences between the Type 6, 7, and 10.
COM Express Type 6
The PICMG COM Express Type 6 standard calls for boards to include:
- Connectors
- AB & CD (Double Row of 220 pins) 440 pins total
- Up to 24x PCI Express Lanes
- 1x PCI Graphics
- 4x SATA Ports
- 1x Gigabit Ethernet
- Display Interfaces
- VDS A & B
- PEG
- Analog VGA
- 3x DDI
- Serial
- 2 TX/RX serial pairs
- USB
- 8x USB 2.0
- 4x USB 3.0
COM Express Type 7
The Type 7 is not a replacement for Type 6, but rather it trades all audio and video interfaces for four 10G Ethernet ports and a total of 32 PCI Express lanes.
- Connectors
- AB & CD (Double Row of 220 pins) 440 pins total
- Up to 32x PCI Express lanes
- 2x SATA Ports
- 10x Gigabit Ethernet
- No Display Interfaces
- Serial
- 2 TX/RX serial pairs
- USB
- 4x USB 3.0
COM Express Type 10
The COM Express Type 10 is intended for low-power platforms like handheld devices. The PICMG COM Express Type 10 standard calls for boards to include:
- Connectors
- AB Single Row
- Up to 4x PCI Express Lanes
- No PCI Graphics
- 2x SATA Ports
- 1x Gigabit Ethernet
- Display Interfaces
- LVDS A only
- 1x DDI
- Serial
- 2 Serial Com
- 1 Optional CAN
- USB
- 8x USB 2.0
- 2x USB 3.0
COM Express Carrier Board Engineering & Manufacturing
Sealevel leverages COM architecture for future-proof technology, long product lifecycle availability, and SWaP-C2 optimization. We’ve designed and manufactured over 100,000 embedded computing solutions since 1994 for customers in defense, public safety, wind energy, oil and gas, and industrial automation. COM architecture allows for the mounting of all connectors directly to the carrier board, eliminating internal cable connections. COM solutions also offer a wide operating temperature range, allowing for fanless operation in many applications. To discuss how COM Express design could benefit your specific application and requirements, contact us.
Categories: